UX/UI Layout Patterns In VR Study
This study intends to identify the UX/UI patterns in VR and how they are related to the traditional UX/UI in 2D apps. The study focuses on non-diegetic UI which means that it studies 2D elements within a 3D environment. The UX behind physical interactions such as grabbing, releasing or moving around have not been considered in this study.
Samples
Oculus

Subjects of analysis
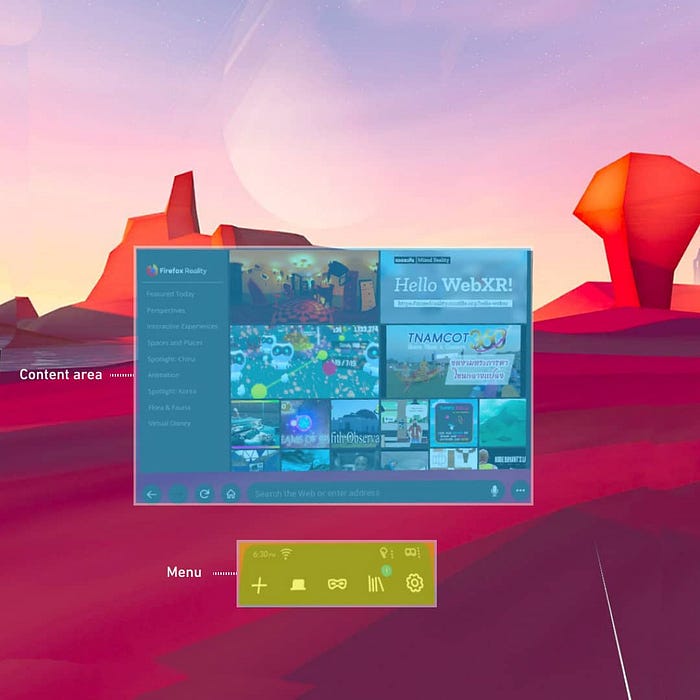
Content area
Menu
Insights
- One column layout
- Two distances. Main menu is closer than content area
- Surrounding background
Youtube VR

Subjects of analysis
Content area
Menu
Insights
- One column layout
- One distance. Main menu and content area are at the same distance from the user
- Neutral background
Altspace VR

Subjects of analysis
Content area
Menu
Insights
- Three column layout
- One distance. Main menu and content area are at the same distance from the user
- Surrounding background
Prime Video VR (Amazon)

Subjects of analysis
Content area
Menu
Insights
- One column layout
- One distance. Main menu and content area are at the same distance from the user
- Surrounding background
Horizon Workrooms (Facebook)

Subjects of analysis
Content area
Menu
Insights
- One column layout
- One distance. Main menu and content area are at the same distance from the user
- Surrounding background
Patterns
Distances

Two main distances are used in the analyzed samples.
Distance 1
Navigation
Content
Panels
Dialogs
Snackbars
Distance 2
Navigation
Content
Panels
Layouts

From one-distance layouts, where all the UI is placed at the same distance and where all the navigation occurs in the same distance too, to two-distance layouts where the UI is placed between different distances and the navigation starts in one distance and ends in the other.
- Menu on the top using the Distance 2
- Menu on the bottom using the Distance 2
- Menu on the left using the Distance 2
- Menu on the bottom using the two distances. Distance 1 for the menu and Distance two for the Content Area.
- Two menus and two content areas using the two distances.
- Menu on the bottom using the Distance 1.
Take aways
Dark mode rules
6 out of 6 samples displayed a dark mode by default. However, Oculus for instance allow users to swap to light mode, which by the way doesn’t use pure white.
Sound effects and music
Sound effects in the interactions as well as sounds in the background fill out the experience. Unlike in traditional 2D apps, sound in VR doesn’t feel out of place.
Background as a new element
The background plays a role in the experience. It could help the user to focus by being neutral or it could be colorful and noisy to surround the user.
Take care of the users’ necks
Heights are definitely an important point to consider. Placing the UI too high results in a very bad experience for the user since they have to look up all the time.
Cut content if you need
When using the three column layout, the panels on the edges can be cut on purpose. This forces the user to turn their head rather than move their eyes since moving their eyes can be uncomfortable.
Easier to point in closer distances
When it comes to pointing with the laser (Cursor), it is easier pointing to closer distances (Distance 1). Pointing on Distance 2 requieres a little bit more aim.
Jumping between distances
Designing throughout different distances could be the biggest challenge for UX/UI designers. However it brings infinite new ways of interacting with UI.
Minimize interruptions using closer distances
The closer distance, aside from being used as a menu, could be used to show content to the user without interrupting the main experience.
Resources

UX for XR with Cornel Hillmann
An interesting workshop about how is the design process in XR nowadays (2022).

Google Sticker Sheet
An old but still useful mini Design System made for VR by Google in 2017.
Thank you very much for reading this. I hope it was inspiring to you!
Finally, If you like, hit the follow button, it will help me a lot to keep creating content like this.
Have a good one!